Shenzhen Alu Rapid Prototype Precision Co., Ltd.
Industry News
- Home
- News
- How to make an injection mold?
Making an injection mold is a complex, precision engineering task typically done by specialists for high-volume production. Molds are usually machined from steel or aluminum to withstand high pressures (thousands of PSI) and temperatures, lasting for hundreds of thousands of cycles. Costs range from $2,000–$100,000+ depending on complexity.
Here are the key steps:
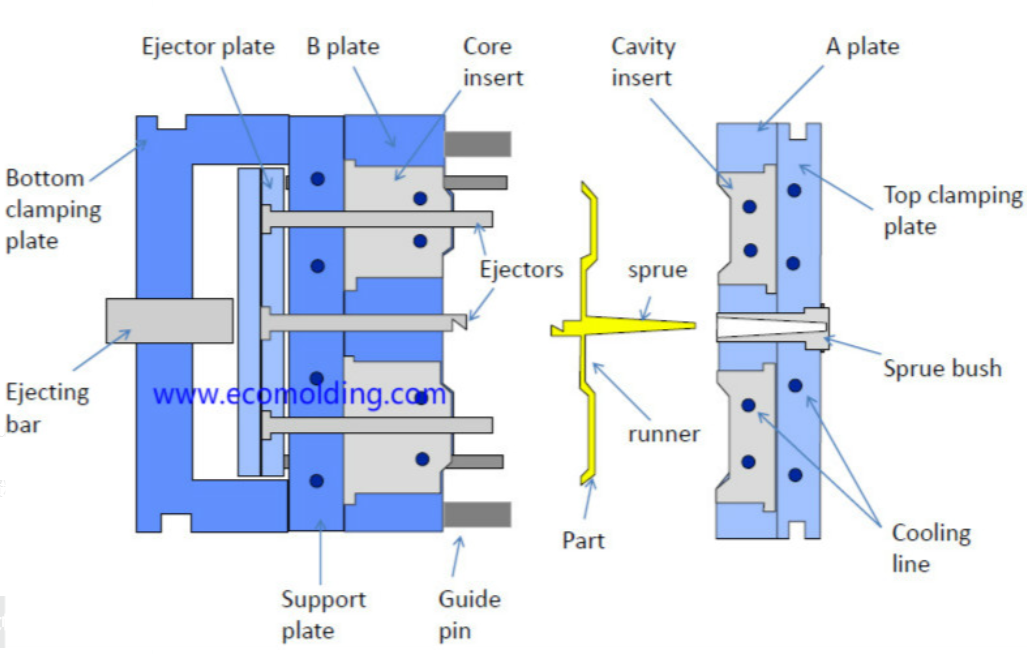
1.Part and Mold Design
Use CAD software to design the plastic part, considering draft angles (for easy ejection), uniform wall thickness, shrinkage (1–2% typically), gates, runners, cooling channels, and ejector pins. Determine the parting line and number of cavities.
2.Material Selection and Procurement
Choose tool steel (e.g., P20 for prototypes, H13 for production) or aluminum for faster machining/softer molds. Order mold base and raw blocks.
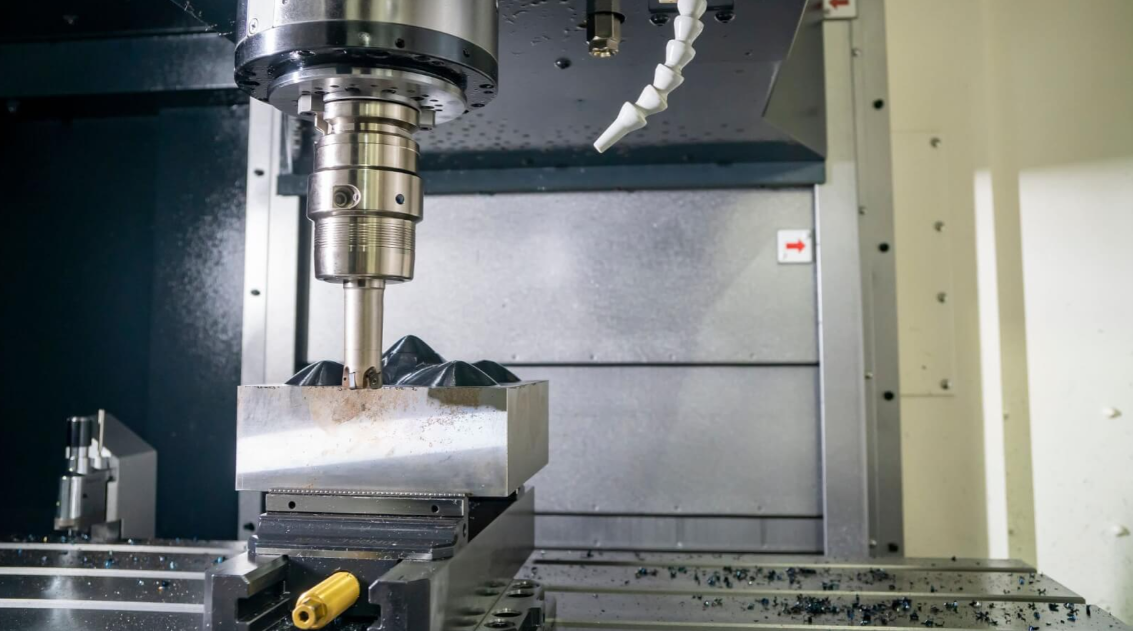
3.Machining the Mold
Rough CNC milling to remove bulk material.
Finish CNC machining for precise cavities/cores.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) for fine details/sharp corners.
Drill cooling lines, ejector holes, and vents.

4.Assembly and Polishing
Fit cores, cavities, slides, and ejectors into the mold base. Polish surfaces for smooth part release and appearance.
5.Testing and Iteration
Run trials on an injection machine, adjust for defects (e.g., warping, flash), and refine.
DIY/Low-Volume Alternatives
For prototypes or small runs (dozens to hundreds of parts), you can make simpler molds at home:
1.3D Printed Molds → Use high-temperature resins (e.g., Formlabs Rigid or High Temp) or tough filaments like PETG-CF. Suitable for benchtop injectors.
2.Machined Aluminum/Soft Metal → Mill with a hobby CNC or manually.
3.Cast Molds → 3D print a pattern, make a silicone mold, then cast resin or low-melt metal.
Example DIY workflow (using 3D printing):
1.Design part and mold in CAD (e.g., Fusion 360 or Blender), adding sprue, vents, and alignment pins.
2.3D print mold halves (cavity facing up to minimize supports).
3.Post-process: Cure, sand, apply release agent.
4.Inject plastic using a manual/desktop machine (e.g., homemade drill-press based or commercial like Galomb/Buster Beagle).
