Shenzhen Alu Rapid Prototype Precision Co., Ltd.
Industry News
- Home
- News
- How thick can you injection mold?
In conventional injection molding, the recommended wall thickness for most plastic parts typically ranges from 1 mm to 5 mm (about 0.04 to 0.2 inches), with the most common and optimal range being 1.5 mm to 3 mm (0.06 to 0.12 inches). This balances material flow, cooling time, strength, and defect prevention.
Thicker walls are possible, but they come with challenges:
1.Standard processes often limit practical maximums to around 5-6 mm to avoid defects like sink marks, voids, warping, uneven shrinkage, and excessively long cycle times.
2.In specialized cases (e.g., optical lenses, filter plates, or high-flow materials like polycarbonate), thicknesses up to 25-114 mm (1-4.5 inches) have been achieved, but these require very long cooling cycles, high pressures, or custom techniques and are not common or cost-effective for most applications.
For truly thick sections, structural foam injection molding is often used instead. This variant introduces a blowing agent to create a dense outer skin with a foamed core, allowing effective wall thicknesses of 6-12 mm (0.25-0.5 inches) or more while reducing weight and sink risks. It's ideal for large, rigid parts like pallets or enclosures.
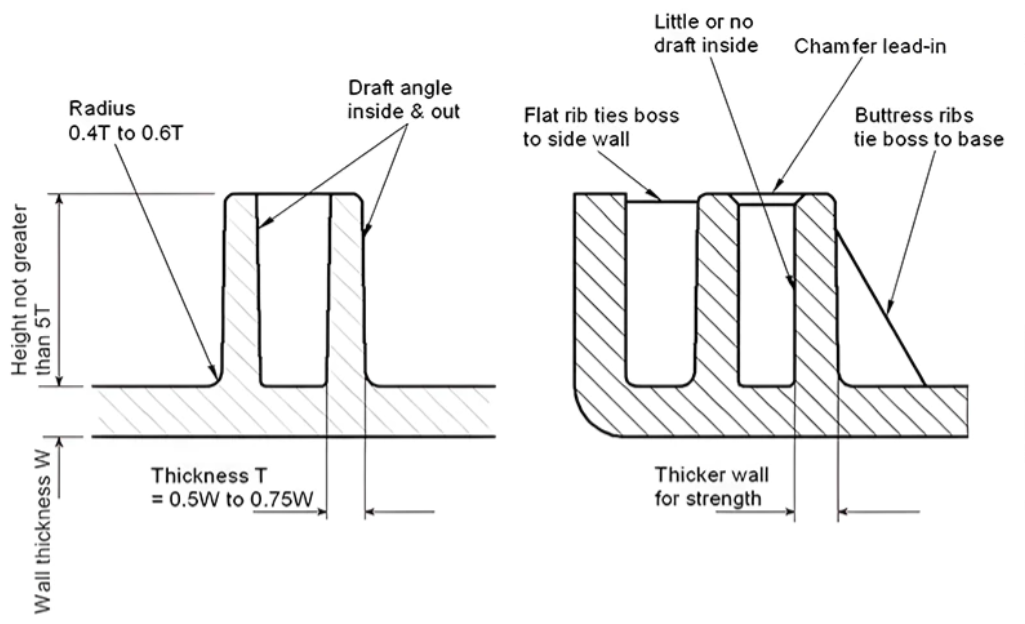
To minimize defects, designers maintain uniform thickness (variations no more than 40-60% between adjacent walls), add ribs/gussets for strength instead of thickening walls, and use mold flow analysis.Here are examples of injection molded part cross-sections and designs illustrating wall thickness considerations (including bosses and ribs in thicker areas):