Shenzhen Alu Rapid Prototype Precision Co., Ltd.
Industry News
- Home
- News
- How to improve die cast mold?
Improving die cast molds (also known as dies or tooling in die casting) focuses on enhancing lifespan, performance, efficiency, part quality, and cost-effectiveness. Die casting involves injecting molten metal under high pressure into a reusable steel mold, so improvements target design, materials, processes, and maintenance to reduce wear from thermal cycling, erosion, and soldering.Optimize Mold Design (Design for Manufacturability - DFM)
1. Optimize Mold Design (Design for Manufacturability - DFM)
Start improvements here, as good design prevents issues downstream.Incorporate sufficient draft angles (1-3° or more) for easy part ejection and reduced wear.
a.Use radii and fillets to avoid stress concentrations and improve metal flow.
b.Optimize cooling channels (e.g., conformal cooling via 3D printing) for uniform temperature distribution, reducing thermal fatigue and cracks.
c.Simulate flow, filling, and stress with software (e.g., Moldflow) to identify hot spots and optimize gates/runners.
d.Allow flexible tolerances and draft in non-critical areas to extend durability.
Recent advances include 3D-printed inserts for complex cooling geometries, improving heat management and mold life.
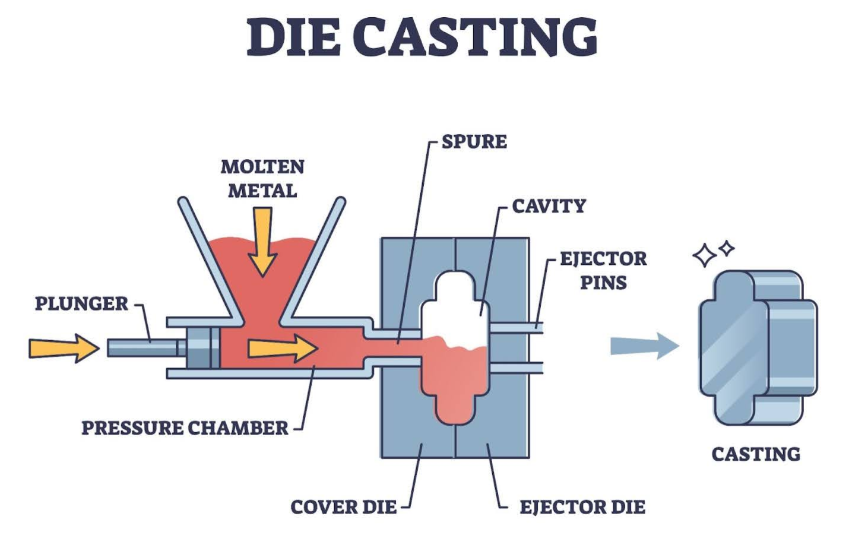
2. Select Premium Materials and Treatments
a.Use high-quality hot-work tool steels like H13, H11, or premium variants (e.g., modified H13 or powdered steels) for better resistance to heat, wear, and fatigue.
b.Apply heat treatments: Quenching, tempering, and nitriding (gas or ion) to increase hardness and toughness.
c.Add surface coatings: PVD (e.g., TiAlN, CrN, AlCrN) or nano-coatings to resist soldering, erosion, and oxidation—can extend life significantly in high-wear areas like gates and cores.
d.For emerging options, explore 3D-printed molds with high-performance powders matching H13 properties.
3. Enhance Cooling and Temperature Control
a.Implement efficient cooling systems to maintain optimal mold temperatures (avoid extremes that cause cracks).
b.Preheat molds properly before production to prevent thermal shock.c3.Use advanced lubricants/release agents that reduce friction without corroding the mold.
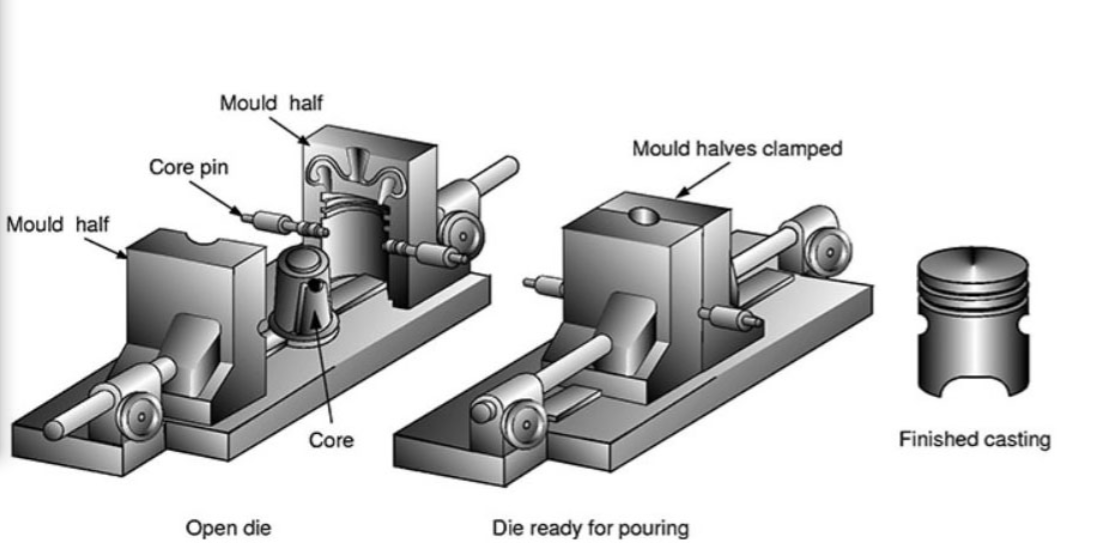
4. Implement Rigorous Maintenance
a.Follow a scheduled program: Regular cleaning, lubrication, inspection of cooling channels, and polishing to prevent pitting.
b.Monitor for wear (e.g., via sensors for temperature/pressure) and repair promptly (e.g., welding cracks).
Store molds properly (e.g., on racks to avoid damage).
c.Proactive maintenance can extend life by 200-500% and reduce downtime by 40-60%.
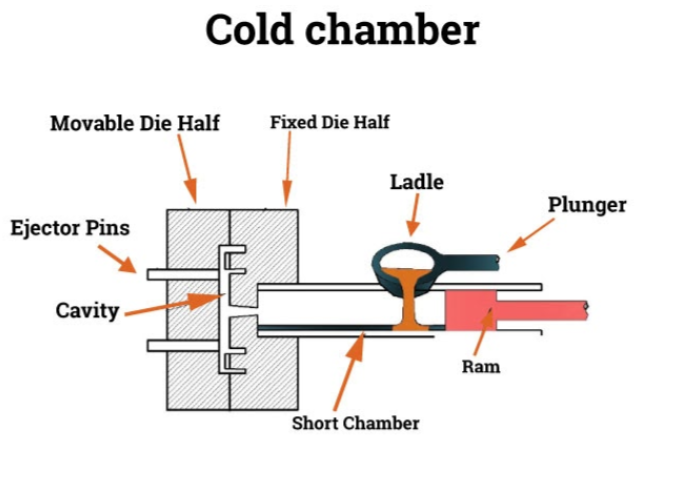
5. Optimize Production Processes
a.Control parameters: Injection speed, pressure, and cycle times to minimize stress.
b.Use high-quality alloys and clean melts to reduce impurities that erode the mold.
c.For zinc die casting, expect longer tool life (up to 1M+ shots) vs. aluminum (~100-200k shots).
Expected Benefits
These improvements can double or triple mold life, reduce defects, lower replacement costs, and boost production efficiency. In 2025-2026, trends like AI-optimized design, IoT monitoring, and additive manufacturing for molds are accelerating gains, especially in automotive/EV applications.
