Shenzhen Alu Rapid Prototype Precision Co., Ltd.
Industry News
- Home
- News
- What are the differences between additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping?
In the context of engineering and manufacturing (and as often tested on Quizlet), the distinction between Additive Manufacturing (AM) and Rapid Prototyping (RP) is primarily about the intent and the outcome, rather than the specific machine used.
While the two terms are often used interchangeably, here is how they differ:
1. Process vs. Application
Additive Manufacturing (The Process): This is the technical umbrella term for any technology that builds objects by adding material layer-by-layer (e.g., 3D printing). It describes how a part is made.
Rapid Prototyping (The Application): This is a specific use case. It describes why a part is being made—to quickly create a physical model to test a design, fit, or function.
2. Scope of Technology
AM is strictly additive. It involves technologies like SLA, FDM, and SLS.
RP is broader. While most rapid prototyping uses additive methods today, it can also include subtractive methods (like high-speed CNC machining) or formative methods (like silicone molding) if they are used to produce a prototype quickly.
Comparison Diagram
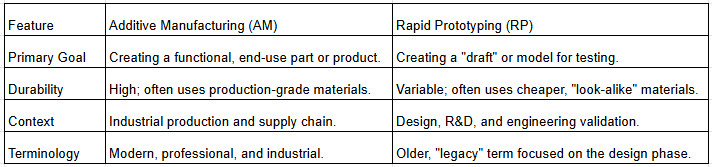
Key Takeaway for a Quiz:
If a question asks which is the official industry standard term for the technology, the answer is Additive Manufacturing. If it asks for the process of quickly fabricating a scale model, the answer is Rapid Prototyping.
