Shenzhen Alu Rapid Prototype Precision Co., Ltd.
Industry News
- Home
- News
- Is die casting an environmentally friendly process?
Die casting is generally considered one of the more environmentally friendly metal manufacturing processes — especially when compared to alternatives like sand casting, machining from solid billets, or plastic injection molding — but it is not perfectly "green". Its environmental performance depends heavily on the material used (aluminum, zinc, magnesium), the energy source, and whether recycled feedstock is utilized.
Key Environmental Advantages of Die Casting
1.Extremely high material recyclability — Aluminum (the most common die casting material) is infinitely recyclable with almost no loss in properties. Using secondary (recycled) aluminum can reduce energy use and CO₂ emissions by ~90–95% compared to primary (virgin) aluminum production.
2.Near-net-shape process → Produces very little scrap/waste compared to machining or sand casting (where large amounts of material are removed or single-use molds create waste).
3.Reusable tooling → Steel dies can produce tens of thousands to millions of parts and can often be retooled or recast instead of scrapped.
4.Long-lasting, lightweight parts → Especially aluminum and magnesium parts help reduce vehicle weight → lower fuel consumption and emissions during the product's use phase (very important in automotive and aerospace).
5.Lower energy per part in high-volume production → Compared to many other metal forming methods when using recycled material.
Here are some typical comparison highlights (aluminum focus):
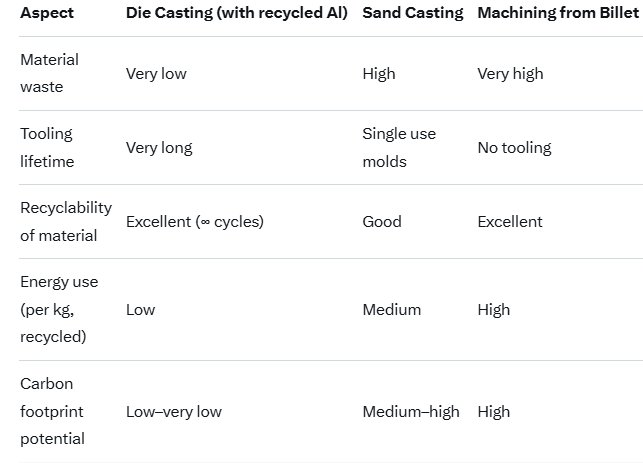
Main Environmental Drawbacks
1.High energy intensity — Melting metal (especially aluminum) requires significant energy. Traditional setups can be energy-intensive and produce emissions if powered by fossil fuels.
2.Primary metal production impact — If virgin aluminum is used, the process has a large carbon footprint due to bauxite mining and electrolysis (very energy-heavy).
3.Emissions & waste — Potential for releases of particulates, VOCs, lubricants, and cooling water use if not managed well.
4.Porosity & rejects — Can generate some scrap (though usually recyclable).
Many leading die casters now:
1.Use 90–98% secondary/recycled metal
2.Implement energy-efficient machines and regenerative systems
3.Switch to renewable electricity sources
4.Adopt closed-loop water systems
5.Achieve ISO 14001 environmental certification
Bottom line (2026 perspective):
Die casting is relatively environmentally friendly — particularly aluminum or zinc die casting using recycled material in high-volume production — and often one of the better choices among metal manufacturing processes. However, it is not inherently "green" if using primary metal and outdated, energy-inefficient equipment.When companies optimize for sustainability (recycled feedstock + modern practices), die casting becomes a very strong option for producing durable, recyclable metal components with a comparatively low overall environmental footprint.
