Shenzhen Alu Rapid Prototype Precision Co., Ltd.
Industry News
- Home
- News
- How to make a prototype mold?
Creating a prototype mold is a key step in product development, especially when you need functional parts that closely match final production quality (e.g. for injection molding, casting, or low-volume production).
The approach you choose depends on:
1.Material you want to mold (plastic, silicone, resin, etc.)
2.Number of parts needed (1–10 vs 50–5,000)
3.Required precision and surface finish
4.Budget & timeline
Here are the most popular modern methods in 2025–2026, with their typical workflows.
Rapid Aluminum Injection Mold (Most Common for Functional Plastic Prototypes)
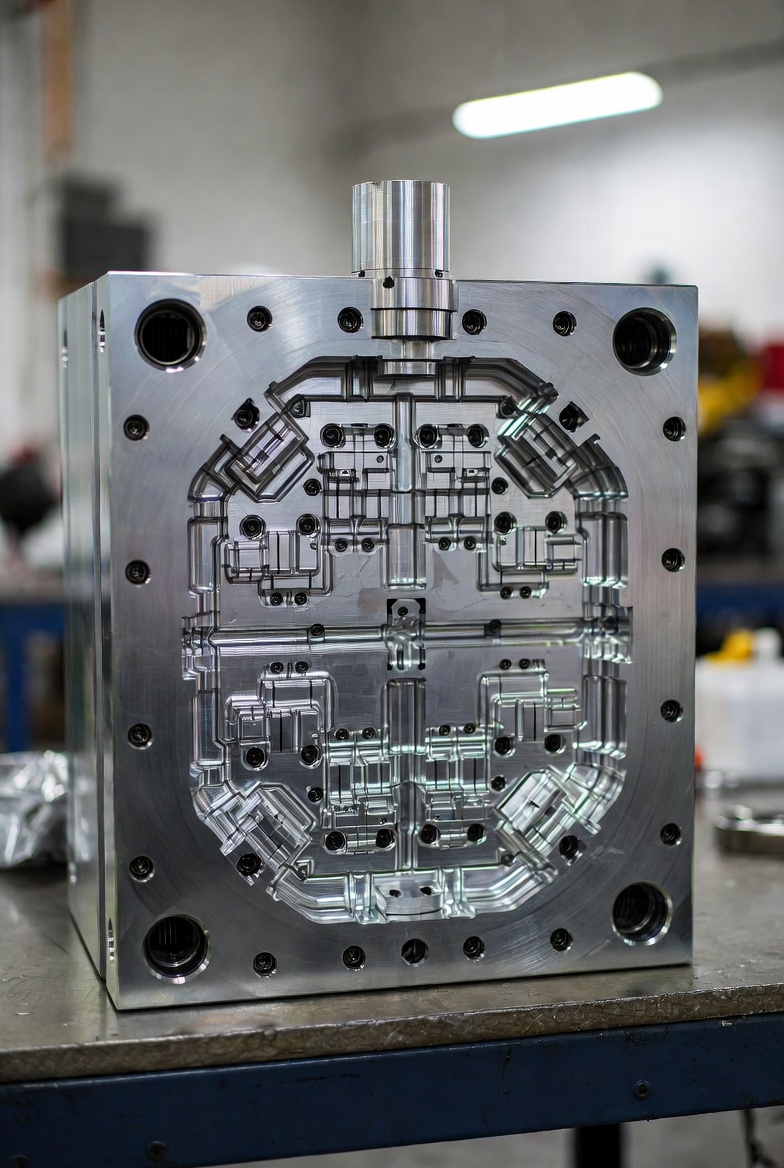
This is the industry standard bridge between concept and mass production tooling. Aluminum molds are much faster and cheaper than steel production molds.Here are some real-world examples of aluminum prototype molds:
Typical Step-by-Step Process:
1.Design the part → Create detailed 3D CAD model + perform DFM (Design for Manufacturability) analysis
2.Mold design → Design the mold (core/cavity, parting line, gates, vents, cooling channels)
3.Material selection → Usually 7075 or 6061 aluminum for prototype molds
4.CNC machining → High-speed CNC mills the mold blocks (sometimes with EDM for very fine details)
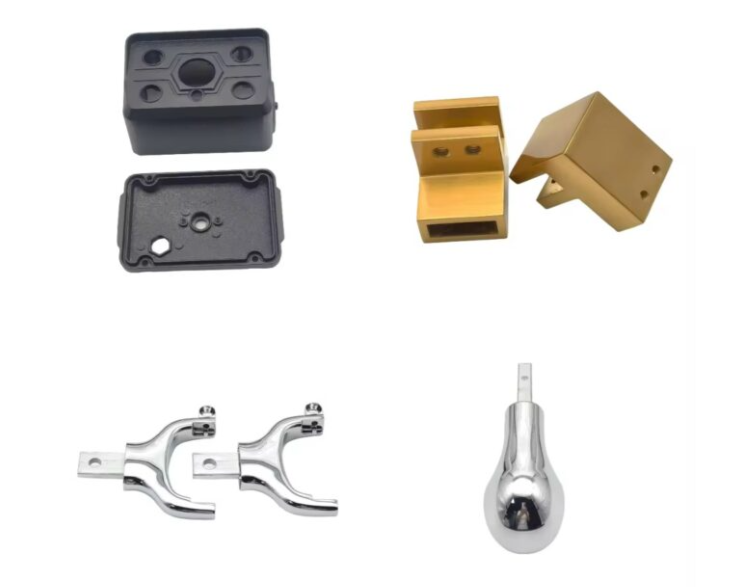
Here’s a precision CNC-machined aluminum prototype mold example:

5.Polishing & texturing → As needed (SPI finishes A1–C3)
6.Mold trial → Install in injection molding machine → First shots (T0/T1)
7.Adjust & optimize → Minor modifications if necessary
8.Produce prototypes → 100–5,000+ shots possible (depending on part complexity & material)
Best for: 50–5,000+ functional plastic parts that look & feel like production
Lead time: 1–5 weeks
Cost: $2,000–$15,000 (much less than production steel mold)
Silicone Mold + Urethane/Resin Casting (Vacuum Casting)
Very popular for 10–100 pieces, excellent surface finish, and quick turnaround.Here are some typical silicone molds used for prototype casting:
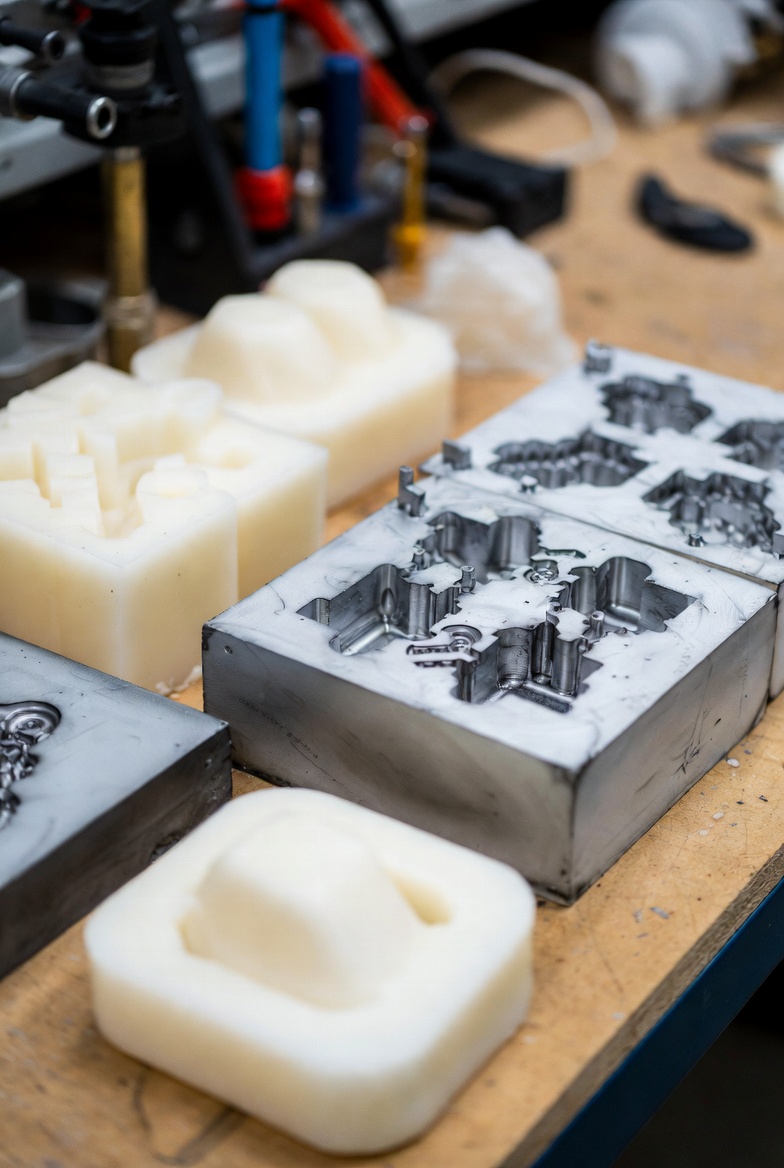
Process:
1.Create master pattern (usually 3D printed SLA, CNC machined, or existing part)
2.3D print or prepare the master
3.Build mold box around master
4.Pour silicone rubber (RTV) → degas in vacuum chamber
5.Cure → cut mold in half (usually 2-part mold)
6.Cast polyurethane/resin/epoxy into silicone mold under vacuum
7.Cure → demold → repeat (one silicone mold usually lasts 15–40 shots)
Best for: Visual models, soft-touch parts, overmolding, small series (10–100 pcs)
Lead time: 3–10 days
Cost: Very affordable ($300–$2,500 for mold + parts)
3D-Printed Mold Inserts (Emerging & Very Fast in 2025–2026)
Modern high-temperature composite 3D printing allows direct printing of mold inserts (or complete small molds) for low-volume injection molding.
Process:
1.Design mold with printable inserts
2.Print using high-temp composite (e.g. carbon-fiber filled, ceramic-filled resins)
3.Post-process (smooth, coat if necessary)
4.Insert into standard mold base
5.Injection mold (usually 50–500 shots max)
Best for: Very fast iterations, complex geometries, ultra-low volume
Lead time: 2–7 days
Cost: Often cheapest for <100 parts
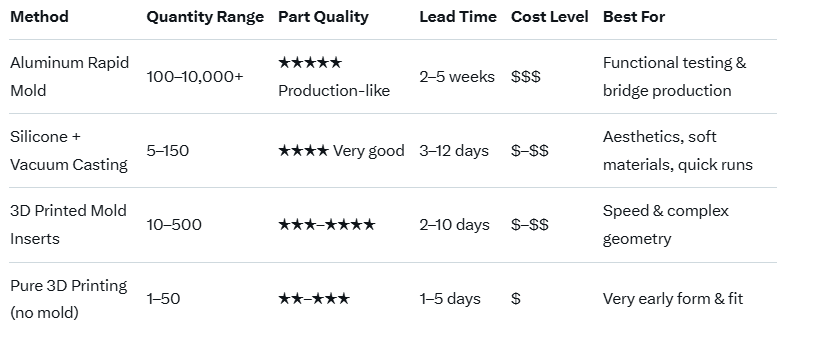
Quick Comparison Table (2025–2026 Reality)