Shenzhen Alu Rapid Prototype Precision Co., Ltd.
Industry News
- Home
- News
- How to calculate the cost of vacuum casting?
Calculating the cost of vacuum casting (also known as urethane casting or polyurethane casting) involves breaking down the project into its main cost components. This method is popular for prototyping and small-batch production (typically 10–100 parts), as it uses soft silicone molds to replicate a master model in liquid polyurethane resin under vacuum.Unlike injection molding, vacuum casting has low upfront tooling costs but the per-part price decreases as quantity increases (due to amortizing the mold cost over more parts).
Main Cost Components
1.Master Model (Pattern) Cost — One-time fee
This is the original part used to create the silicone mold. Usually made by SLA 3D printing, SLS, CNC machining, or sometimes existing parts.
Cost: $50–$800+ (very roughly), depending on size, complexity, required surface finish, and method.
High-quality surface finish is critical — any defects will replicate in every cast part.
If you already have a suitable master, this cost can be $0.
2.Silicone Mold (Tooling) Cost — One-time fee per mold Made by pouring liquid silicone around the master pattern.
Cost: Typically $200–$1,200 per mold (most common range $300–$800).
Factors that increase mold cost: Part volume/size (more silicone needed)
Complexity (undercuts → split molds or extra parting lines)
Number of cavities (rarely more than 1–2 in vacuum casting)
Mold lifetime: Usually 10–30 shots (copies) depending on geometry, material, and care. High-temp or reinforced silicone can reach 50+ shots.
3.Per-Part Casting Cost (recurring)
This includes resin + labor + finishing per piece. Material (polyurethane resin): $5–$50+ per kg, depending on type (ABS-like, clear, flexible, high-temp, flame-retardant, etc.).
Typical part uses 50–500 g → material cost $1–$25 per part.
Labor (mixing, pouring, demolding, curing, trimming): $5–$40+ per part.
Post-processing (sanding, painting, assembly, inserts, texturing): $0–$50+ per part.
Typical per-part range (after mold is made): $10–$100 (simple small parts $10–$40; medium/complex $40–$100+).
4.Overhead & Other Costs (often 10–30% of total)
Machine time, electricity, facility costs, packing, shipping.
Basic Cost Calculation Formula
Total Project Cost = Master Cost + Mold Cost + (Per-Part Cost × Quantity)Average Cost per Part = (Master Cost + Mold Cost) / Quantity + Per-Part Cos
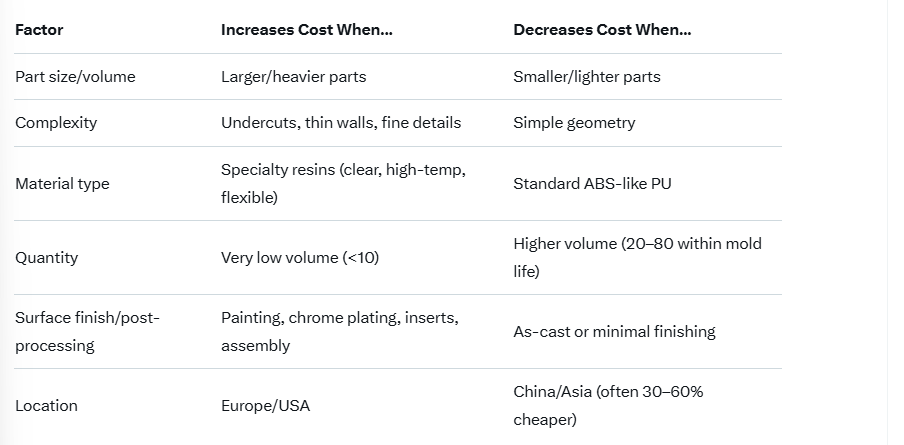
Key Factors That Increase/Decrease Cost