Shenzhen Alu Rapid Prototype Precision Co., Ltd.
Industry News
- Home
- News
- How strong is 3d printed material?
The strength of 3D-printed parts varies enormously — from “weaker than cheap packaging foam” to “stronger than machined aluminum” — depending on several key factors. Here’s a practical breakdown:
1. Printing Technology Matters Most
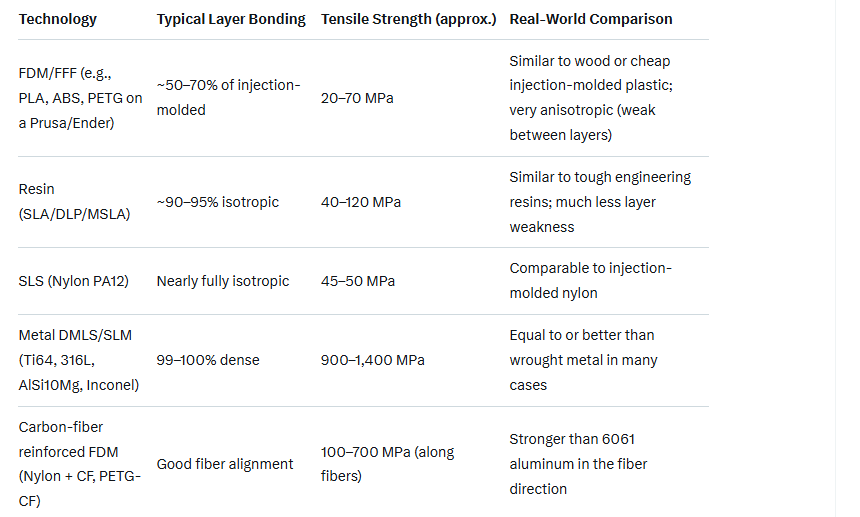
2. Layer Adhesion = The Achilles’ Heel of FDM
In consumer FDM, parts are typically only 30–70% as strong between layers as within a layer. A 60 MPa PLA part printed with good settings might fail at only ~20–30 MPa if you pull perpendicular to the layers (like peeling apart a lasagna).
Tricks to dramatically improve FDM strength:
a.Use high-temperature materials (ASA, PC, Nylon) and a heated chamber or enclosure → can reach 80–90% layer bonding
b.Anneal the part after printing (e.g., 110 °C for PLA, 90–120 °C for Nylon)
c.Print slower, hotter nozzle, higher bed temp
d.Use 100% infill + many perimeters or gyroid infill
e.Add continuous carbon-fiber (Markforged, Anisoprint) → parts can hit 700+ MPa in fiber direction, rivaling aluminum
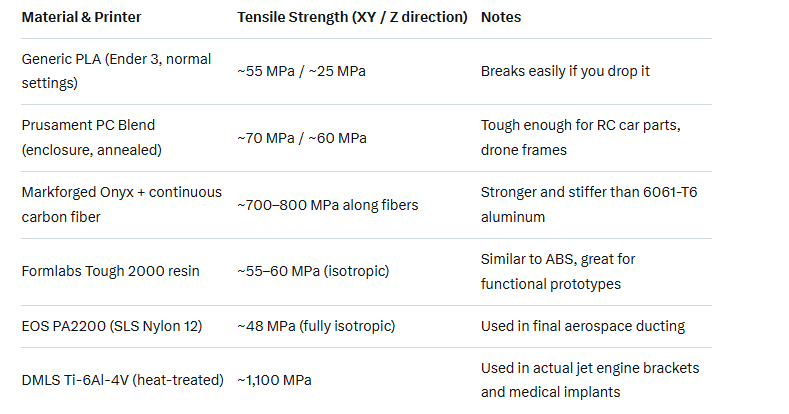
3. Real-World Examples (tested values)